Rh grouping :
- Another antigen, the Rh antigen similar to one present in Rhesus monkeys (hence Rh), is also observed on the surface of RBCs on majority (nearly 80 %).
- Person with Rh antigen is said to be Rh positive (Rh+).
- Person without Rh antigen is said to be Rh negative (Rh-).
- Person with Rh- blood transfused with Rh+ blood, forms anti Rh antibody and destroy the Rh+ RBCs.
- A special case of Rh incompatibility (mismatching) has been observed between the Rh- bloods of pregnant mother with the Rh+ blood of the foetus.
- During parturition the Rh+ foetal blood mixed with the Rh- maternal blood, hence anti Rh antibody formed in mothers blood.
- In successive pregnancy the anti Rh antibody from mother’s blood leaks into the foetal blood and destroy the Rh+ RBCs.
- This caused HDN (haemolytic disease in new born) or Erythroblastosis foetalis.
- This can be prevented by administering anti-Rh antibody to the mother immediately after the delivery of the first child.
COAGULATION OF BLOOD :
- Injury to the blood vessel leads to loss of blood called haemorrhage.
- There is an intrinsic mechanism to stop haemorrhage is called haemostasis or coagulation of blood or blood clotting.
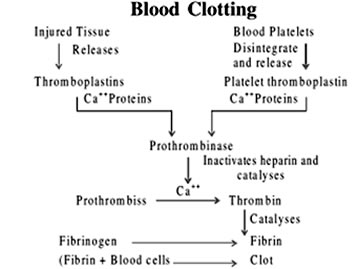
- Clot or coagulum is formed mainly of a network of threads called fibrins in which dead and damaged formed elements of blood are trapped or entangled.
- Fibrin is formed by the conversion of inactive fibrinogens in the plasma by an enzyme called thrombin.
- Thrombin formed from inactive prothrombin of the plasma due to presence of enzyme thrombokinase.
- All these activation required the initial clotting factor called thromboplastin either released from the injured tissue or platelets.
- Calcium ions play a very important role in the coagulation of blood.
Lymph
- The colorless mobile fluid connective tissue drains into the lymphatic capillaries from the intercellular spaces.
Composition :
- It is composed of fluid matrix, plasma, white blood corpuscles or leucocytes.
- Contains less amount of protein than plasma.
- Devoid of RBCs.
Functions :
- It drains excess tissue fluid from extra cellular spaces back into the blood.
- It contains lymphocytes and antibodies.
- It transport digested fats.
CIRCULATORY PATHWAYS :
Open circulatory system :
- Found in arthropods and mollusks.
- Blood from the heart pumped into the open spaces in the body cavity called sinuses.
- The body cavity remained filled with blood (haemolymph) called haemocoel.
Closed circulatory system :
- Found in annelids, echinoderms and all chordates.
- Blood from the heart pumped into definite blood vessels.
- Blood circulated in a wide network of blood vessel throughout the body.
- Blood circulated in a regulated manner.


