BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION
POINTS TO REMEMBER :
- Blood: A special connective tissue that circulates in principal vascular system of man and other vertebrates consisting of fluid matrix, plasma and formed elements.
Plasma :
- The liquid part of blood or lymph which is straw coloured, viscous fluid constituting nearly 55 per cent of blood.
- 90-92 percent of plasma is water and 6-8% proteins.
- Fibrinogen, globulin and albumins are the major protein found in plasma.
- Fibrinogen is required in blood clotting or coagulation of blood.
- Globulins involved in defense mechanism of the body.
- Albumin helps in osmotic balance of blood.
- Plasma also contains small amounts of minerals, glucose, amino acids, lipids etc.
- Plasma without the clotting factors is called serum.
Formed elements :
Erythrocytes :
- Also known as RBC (red blood cells) is the most abundant of all the cells of blood.
- 5 – 5.5 million RBC found per mm-3 of the blood.
- Produced from the red bone marrow in the adult.
- RBCs devoid of nucleus in most of mammals.
- Biconcave in shape
- Red in color due presence of complex conjugated protein called haemoglobin.
- 12-16 gm of haemoglobin present per 100 ml of blood in a healthy adult.
- RBCs have average life span of 120 days after which is destroyed in the spleen.
- Spleen is commonly known as the graveyard of RBCs.
Leukocytes :
- Also known as white blood cells (WBC).
- They are colorless due to lack of haemoglobin.
- They are nucleated and relatively lesser in number which averages 6000-8000 mm-3 of blood.
- We have two main category of WBC;
- Granulocytes
- Neutrophils
- Basophils
- Eosinophils
- Agranulocytes.
- Neutrophils (60-65%) of the total WBCs are phogocytic in nature.
- Basophils (0.5-1 %), secretes histamine, serotonin and heparin and also involved in inflammatory reactions.
- Eosinophils (2-3 %) resist infection and also associated with allergic reaction.
- Lymphocytes (T cells and B cells) constitute 20-25 percent and involved in the immune response of the body.
- Monocytes (10-15%), becomes macrophages.
Thrombocytes :
- Also known as blood platelets.
- Produced from fragmentation of megakaryocytes.
- Blood normally contain 1, 500, 00 – 3, 500, 00 platelets mm-3.
- Involved in releasing thromboplastin required to initiate blood coagulation.
BLOOD GROUPS :
- Two blood grouping mechanisms ABO and Rh system.
ABO grouping :
- ABO grouping is based on the presence or absence of two surface antigens on the RBCs namely A and B.
- Plasma of different individuals contains two natural antibodies, anti ‘A’ and ‘B’.
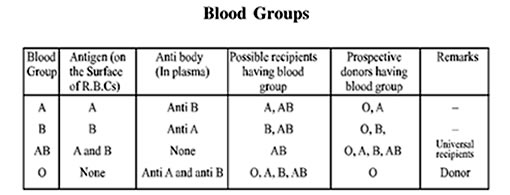
- In a mismatched transfusion the antigen of the donor reacts with antibody of the recipient to cause a reaction called clumping of agglutination.
- Person with blood group ‘O’ has no antigen hence can donate blood anybody, called universal donor.
- Person with blood group ‘AB’ has no antibody in his plasma hence can receive blood from anybody, called universal recipient.
CBSE Biology (Chapter Wise) Class XI ( By Mr. Hare Krushna Giri )
Email Id : [email protected]
Biology - Mr. Hare Krushna Giri


