Carbon and Its Compounds
CARBON
- An element
- A non-metal
- Present in earth’s crust- 0.02% ( in form of minerals – carbonates, coal, petroleum, etc.) an din atmosphere – 0.03% ( CO2 )
- Present in all living things – ( Carbon compounds---- Organic Compounds)
- Always forms Covalent bonds.
- Is tetravalent
- Occurs in both free and combined state.
COVALENT BONDS
At. no. is 6 ---- K-2 ; L-4 ----- To become stable it should either gain 4 electrons or lose 4 electrons.
- It cannot gain 4 electrons - It would be difficult for nucleus with 6 protons to hold 10 electrons.
- It cannot lose 4 electrons - It would require large amount of energy to remove 4 electrons .
This problem is overcome by sharing its valence electrons with other atoms of carbon or with atoms of other elements.
- Covalent bonds are very strong and do not break easily because the carbon atoms are very small in size due to which their nuclei hold the shared pair of electrons between atoms strongly .
CARBON IS TETRAVALENT
Tetra - 4 ; Valent – valency 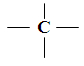
SELF COMBINATION ( Catenation)
Carbon atoms form long chains which are useful to us as we can derive large no. of carbon compounds.
- Carbon compounds are exceptionally stable as they form strong bonds among themselves and with other elements.
OCCURRENCE OF CARBON
- In free state --- Diamond , Carbon, Buckminsterfullerene
- In combined state ---- In form of compounds
- CO2 in air
- Carbonates ( limestone, marble, chalk)
- Fossil fuels ( coal , petroleum, natural gas)
- Organic compounds ( carbohydrates, fats and proteins)
- Wood, cotton wool, etc.
ALLOTROPES OF CARBON
The various physical forms in which an element can exist.
- Diamond ----- Colourless , transparent substance with extraordinary brilliance.
Extremely hard , heavy, does not conduct electricity, burns on strong heating to give CO2 , high melting point ( more than 3500°C )
Structure of Diamond
Each carbon atom in the diamond crystal is linked to four other carbon atoms by strong
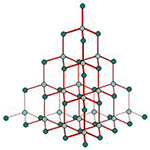
covalent bonds and forms a regular tetrahedron. Due to this the structure gets very rigid .
Uses of Diamond
- Making rock borers for drilling oil wells
- Making glass cutters
- For jewellery making
- For removing cataract from eyes.
- Diamonds can also be made artificially by subjecting pure carbon to very high pressure and temperature . Theses are also called Synthetic diamonds.
Submitted By Mrs. Kritika Bhola
Email Id : [email protected]
![]()
