![]()
CBSE Guess > Papers > Important Questions > Class X > 2008 > Science > Science By :- Nagesh Kumar
Science - Electricity
- What is electric current?
- What is the SI unit of electric current?
- What is the SI unit of electric charge?
- What is ohm’s law? Give its mathematical expression?
- How much current will an electric heater coil draw from a 220 volt line, if the resistance of the heater coil is 40
 ?
? - Calculate the number of electrons constituting one coulomb of charge.
- The potential difference between the terminals of an electric heater is 30 volt when it draws current of 4 A from the source. What current will the heater draw if the potential difference is increased to 120 volt?
- A current of 4 A exists in a 10
 resistor for 4 minute. Find the charge and the number of electrons that pass through any cross-section of the resistor in this time
resistor for 4 minute. Find the charge and the number of electrons that pass through any cross-section of the resistor in this time - Why are metals able to conduct electricity
- How should the resistances be connected so that the equivalent resistance is increased?
- The combination of resistances shown below has equivalent resistance equal to 12 ohm, what is the value of R?
- Which metal is the best conductor of electricity at room temperature?
- Calculate the amount of charge that would flow in 1 hour through the elements of an electric bulb drawing a current of 0.4 A.
- What is the power of an electric lamp, if it draws 20 A current when connected to 220 V line?
- To produce 1000 joule of heat in 10 seconds, how much voltage should be applied to 50
 resistance.
resistance. - In the circuit diagram given below, find the equivalent resistances and total current flowing through the circuit.
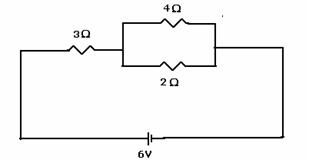
- a) State the law, which relates the current in a conductor to the potential difference across its ends.
- Draw the V-I graphs for a
- A simple electric circuit has 24 V batteries and a resistor of 30 ohm. What will be the current in the circuit?
- What is a magnet?
- What is the SI unit of induced current?
- What is the frequency of d.c current?
- What is the principle on which working of electric generator is based? What are their important parts?
- Why two magnetic lines of forces don’t intersect each other?
- Give two methods with which we can increase the strength of magnetic field produced by a circular coil carrying current?
- State the following laws:
- Maxwell’s right hand rule.
- Fleming’s left hand rule
- Fleming’s right hand rule.
- What do you mean by electromagnetic Induction? Explain the induction of current in the secondary coil with change in current in primary coil.
- Distinguish between an electric motor and generator?
- What are the factors which govern the force experienced by a current carrying conductor placed in a uniform magnetic field depends?
- What is the frequency of a.c current that you use in your house?
- What is magnetic field?
- There is a battery operated toy, what kind of motor is being used in it?
- Give two example of devices in which d.c motor is used.
- Give two examples in which a.c motor is used.
- What will be the frequency of an alternating current, if its direction changes after every 0.05 sec?
- What is direct current (d.c) and alternating current (a.c).
- What is the principle behind the working of electric generator? Explain its working with the help of well labeled diagram.
![]()
