Q. 1. HC1 and HNO3 both produce hydrogen ions in aqueous state. With metals they produce hydrogen gas. However, as HNO3 is a strong oxidising agent, it reacts with the hydrogen gas so produced during the reaction to form water. Thus, acids such as HC1, H2SO4 produce hydrogen gas with metals whereas, HN03 produce water.
Q. 2.
| Minerals | Ores | Gangue |
| Substances that occur naturally in rocks and have their own characteristic appearance and chemical composition . | Minerals, from which the metals can be profitably extracted, are called ores. | Waste materials, which are mixed in the valuable ores. |
| All minerals are not ores. | All ores are minerals. |
Q. 3. Metal A is Zn.
It reacts with blue copper sulphate to form colourless zinc sulphate.
Zn(s)+CuSO4 (aq)→ ZnSO4 (aq)+Cu(s)↓
Copper sulphate zinc sulphate (Brown)
(Blue) (Colourless)
It reacts with green iron sulphate to produce colourless zinc sulphate.
Zn(s)+FeSO4 (aq)→ZnSO4 (aq)+Cu(s)↓
Ferrous sulphate zinc sulphate (Brown)
(Green) (Colourless)
Zn does not react with aluminium hydroxide, as Zn is less reactive than Al, hence it cannot displace it.
Q. 4. Highly reactive elements are obtained by the electrolysis of their molten chlorides. The metals are deposited at the cathode, whereas, chlorine is liberated at the anode. In the case of sodium chloride, the reactions are: At cathode, Na+ + e- → Na At anode, 2Cl- → Cl2 + 2e- Similarly, aluminium is obtained by the electrolytic reduction of aluminium oxide. Carbon cannot be used for the reduction of highly reactive metals because these metals have more affinity for oxygen than carbon. These metals are obtained by electrolytic reduction.
Q. 5. 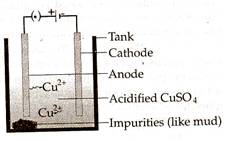 Electrolytic refining is the process of obtaining metals of very high purity by depositing the desired metal and the impure metal on different electrodes in an electrolytic cell. Metal obtained after reduction are not very pure, so they need to be refined further. The most widely used method is electrolytic refining. For example, in the electrolytic refining of copper, CuSO, is acidified (to make it highly conducting) and is used as electrolyte. The anode is made of thick impure copper rod, whereas the cathode is made of thin pure copper. Anode is connected to positive terminal of the battery whereas cathode is connected to the negative terminal of the battery. Pure metal is obtained at cathode.
Electrolytic refining is the process of obtaining metals of very high purity by depositing the desired metal and the impure metal on different electrodes in an electrolytic cell. Metal obtained after reduction are not very pure, so they need to be refined further. The most widely used method is electrolytic refining. For example, in the electrolytic refining of copper, CuSO, is acidified (to make it highly conducting) and is used as electrolyte. The anode is made of thick impure copper rod, whereas the cathode is made of thin pure copper. Anode is connected to positive terminal of the battery whereas cathode is connected to the negative terminal of the battery. Pure metal is obtained at cathode.
Q. 6. Corrosion is the wearing away, dissolving, or softening of any substance which takes place due to chemical or electrochemical reaction with its environment. It applies to the gradual action of natural agents, such as air or salt water, on metals. It is rather a slow process. Four methods used to prevent from corrosion are: