CBSE Guess > Papers > Important Questions > Class XII > 2011 > Computer Science > Computer Science By Deepa
CBSE CLASS XII
Arrays (Questions with Answer)
Page 2 of 3
- Write a user-defined function named Upperr_half() which takes 2D array A, with size N rows and N columns as argument and prints the lower half of the array
Eg.Input
2 3 1 5 0
7 1 5 3 1
2 5 7 8 1
0 1 5 0 1
3 4 9 1 5
the output will be
2 3 1 5 0
1 5 3 1
7 8 1
0 1
5
Ans.
void Upper_half(int a[10][10],int n)
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{ cout<<endl;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
if(i<=j)
cout<<a[i][j]<<" ";
else
cout<<” “;
}
}
- Write UDF in C++ which accepts an integer array and its size as arguments/ parameters and assign the elements into a 2 D array of integers in the following format:
If the array is 1,2,3,4,5.
The resultant 2D array is given below
1 0 0 0 0
1 2 0 0 0
1 2 3 0 0
1 2 3 4 0
1 2 3 4 5
Ans:
void assign_lower_half(int a[10],int n)
{
int b[10][10],i,j;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
if(i>=j)
b[i][j]=a[j];
else
b[i][j]=0;
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{ cout<<endl;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
cout<<b[i][j]<<" ";
}
}
- Write function in C++ which accepts an integer array and size as arguments and assign values into a 2D array of integers in the following format :
If the array is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
The resultant 2D array is given below
1 2 3 4 5 6
1 2 3 4 5 0
1 2 3 4 0 0
1 2 3 0 0 0
1 2 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0
Ans:
void r_upper_half(int a[10],int n)
{ int b[10][10],i,j;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
if(i+j<=n-1)
b[i][j]=a[j];
else
b[i][j]=0;
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{ cout<<endl;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
cout<<b[i][j]<<" ";
}
}
- Write a function in C++ which accepts an integer array and its size as arguments/ parameters and then assigns the elements into a two dimensional array of integers in the following format:
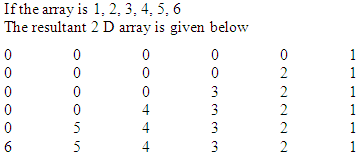
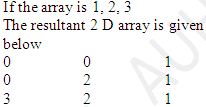
Ans.
void r_lower_half(int a[10],int n)
{
int b[10][10],i,j,k=n-1;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
if(i+j>=n-1)
b[j][i]=a[k];
else
b[i][j]=0;
k--;
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{ cout<<endl;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
cout<<b[i][j]<<" ";
}
}
- Write a function in C++ which accepts an integer array and its size as arguments/parameters and assigns the elements into a two dimensional array of integers in the following format.
if the array is 9,8,7,6,5,4 .
The resultant 2D array is given below
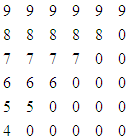
if the array is 1, 2, 3.
The resultant 2D array is given below
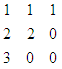
Ans:
void r_upper_half(int a[10],int n)
{
int b[10][10],i,j;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
if(i+j<=n-1)
b[i][j]=a[i];
else
b[i][j]=0;
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{ cout<<endl;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
cout<<b[i][j]<<" ";
}
}
- Write a function in C++ which accepts a integer array and its size as an arguments and prints the output (using nested loops) in following format :
Example : if the array is having1 2 4 5 7.
Then the output should be
1
2 2
4 4 4 4
5 5 5 5 5
7 7 7 7 7 7 7
Ans.
void r_lower_half(int a[10],int n)
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{ cout<<endl;
for(j=1;j<=a[i];j++)
cout<<a[i]<< " ";
}
}
- Write a function in C++ which accepts an integer array and its size as arguments/parameters and assign the elements into a two dimensional array of integers in the following format (size must be odd)
If the array is 1 2 3 4 5 .
The output must be
1 0 0 0 5
0 2 0 4 0
0 0 3 0 0
0 2 0 4 0
1 0 0 0 5
If the array is 10 15 20.
The output must be
10 0 20
0 15 0
10 0 20
Ans:
void diagonal(int a[10],int n)
{
int b[10][10],i,j,k1=0,k2=n-1;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(i==j)
{
b[i][j]=a[k1];
k1++;
}
if(i+j==n-1)
{
b[i][j]=a[k2];
k2--;
}
if(i!=j&&i+j!=n-1)
b[i][j]=0;
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{ cout<<endl;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
cout<<b[i][j]<<" "; }
}
- Write a function in c++ which accepts a 2D array of integers, number of rows and number of columns as arguments and assign the elements which are divisible by 3 or 5 into a one dimensional array of integers.
If the 2D array is
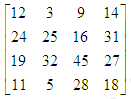
The resultant 1D arrays is 12 , 3 , 9 , 24 , 25 , 45 , 9 , 5 , 18
Ans.
void assign2dto1d(int a[10][10],int m,int n)
{
int b[10],i,j,k=0;
for(i=0;i<m;i++)
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]%3==0||a[i][j]%5==0)
{
b[k]=a[i][j];
k++;
}
}
cout<<"\nThe resultant 1D array is :";
for(i=0;i<k;i++)
{ cout<<b[i]<<" ";}
}
- Write a function in C++ which accepts a 2D array of integers and its size as arguments and displays elements which are exactly two digit number.
If 2D array is
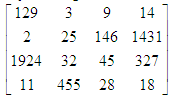
Output is : -
14 25 32 45 11 28 18 Ans.
void twodigit(int a[10][10],int m,int n)
{
int i,j;
cout<<"\nThe output is: ";
for(i=0;i<m;i++)
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]>9 && a[i][j]<100)
cout<<a[i][j]<<" ";
}
}
- Let A[M X M] be a two dimensional array. Write a function in C++ to find the sum of all the positive elements, which lie on either diagonal. For example, for the matrix shown below, your function should
output 43 = (11 + 4 + 12 + 7 + 9):
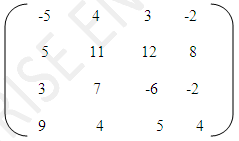
Ans.
void twodigit(int a[10][10],int m,int n)
{
int i,j,sum=0;
cout<<"\nThe output is: ";
for(i=0;i<m;i++)
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{ if(i==j||i+j==n-1)
if(a[i][j]>0)
sum+=a[i][j];
}
cout<<"The output is:"<<sum;
}
  
Submitted By Deepa
Email Id : [email protected]
About Author: Computer Teacher From Sunrise English Pvt. School |
|