CBSE Guess > Papers > Important Questions > Class X > 2012 > Science > Science By Mr. Sunil D Chauhan
CBSE CLASS X
Chemical Reaction
- Why do potato chips manufacturers fill the packet of chips with nitrogen gas?
- A student has been colleting silver and copper coins. One day he observed that a black coating on silver coins and a green coating on copper coins. Give the chemical names of the black and green coatings. How are they formed?
- Tap water conducts electricity whereas distilled water does not. Explain, Why?
- Five metals A, B, C, D and F are added to the following solutions one by one. The observations made are below :
Metal |
Iron(II) sulphate |
Copper(II) sulphate |
Zinc sulphate |
Silver nitrate |
Aluminium sulphate |
A |
No reaction |
Reddish brown deposit |
Coating on it |
Coating on it |
--- |
B |
Grey deposit |
--- |
No reaction |
Coating on it |
--- |
C |
No reaction |
No reaction |
No reaction |
White deposit |
--- |
D |
No reaction |
No reaction |
No reaction |
No reaction |
No reaction |
E |
--- |
Reddish brown deposit |
New coating |
New coating |
No reaction |
Answer the following questions based on above observations-
- Which is the most active metal and which is the least reactive? Why?
- What would be observed when (a). B is added to a solution of copper (II) sulphate and (b). E is added to the solution of iron sulphate? Explain, why?
- Arrange the metals A, B, C, D and E in order of increasing reactivity.
- Container of which metal can be used to store both zinc sulphate solution and silver nitrate solution.
- Which of the above solutions can be easily stored in a container made up of these metals?
- Identify the type of chemical reaction taking place in each of the following–
- Barium chloride solution is mixed with copper sulphate solution and a white precipitate is formed.
- On heating copper powder in air in a china dish, the surface of the copper powder turns black.
- On heating green coloured sulphate crystals, reddish brown solid is left and smell of gas having odour of burning sulphur is experienced.
- White silver chloride turns grey in sunlight.
- Barium hydroxide reacts with ammonium chloride solution to give ammonia, barium chloride and water.
- Iron nails when left dipped in blue copper sulphate solution become brownish in colour and the blue colour of copper sulphate fades away.
- Quick lime reacts vigorously producing a hissing sound with water releasing a large amount of heat.
- What is the colour of ferrous sulphate crystals? How does this colour change after heating? Name the products formed on strongly heating ferrous sulphate crystals. What type of chemical reaction occurs in this change?
- What is an oxidation reaction? Give an example. Is oxidation an exothermic or endothermic reaction?
- Define combustion reaction. Give an example of combustion reaction which is also exothermic.
- Why should magnesium wire be cleaned before burning in air?
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction which is used in black and white photography.
- In electrolysis of water, why is the volume of gas collected over one electrode is double that of gas collected over the other electrode?
- What is observed when a solution of potassium iodide is added to a solution of lead nitrate taken in a test tube? What type of reaction is this? What is the colour of the product formed? Write a balanced chemical equation to represent the above reaction.
- Crystals of copper sulphate are heated in a test tube. What is the colour of the copper sulphate crystals before and after heating? What is the source of liquid droplets seen on the upper inner side of test tube during heating?
- State which of the chemical reactions will take place or not, giving suitable reason for each –
Zn (s) + CuSO4 (aq) ------> ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
Fe (s) + ZnSO4 (aq) ------> FeSO4 (aq) + Zn (s)
Zn (s) + FeSO4 (aq) ------> ZnSO4 (aq) + Fe (s)
- Why do ionic compounds conduct electricity in aqueous solution and not in solid state?
- Identify the type of chemical reaction in
Na2 SO4 (aq) + BaCl2 (aq) ------>BaSO4 (s) + NaCl (aq).
- What happens to the crystals of sodium carbonate, if they are (i). left open in air, (ii). heated? Write chemical equations to support your answer.
- State electrolytic decomposition with the help of an example.
- What are the effects of oxidation reaction in everyday life? Define these terms with an example each.
- Balance the following chemical reactions –
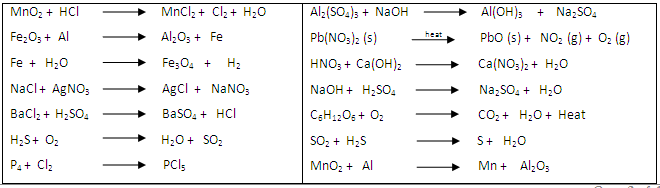
- What are the decomposition reaction, combination reaction, precipitation reaction, endothermic reaction, exothermic reaction, thermal decomposition reaction, displacement reaction and double displacement reaction? Explain each with one example?
- A person wanted his house to be whitewashed. He bought 15 Kg of quick lime and dissolved it in 30 liters of water. On adding lime to water he noticed that the water started boiling even when it was not being heated. Hive reason for his observation. Write the corresponding chemical equation and name product formed.
- Which one of the following reaction is combination reaction -
(a) a magnesium wire is burnt in air,
(b) limestone is heated,
(c)proteins are converted into amino acids and
(d) electricity is passed through water.
- Which type of reactions are represented by the following equations-
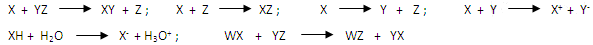
- What are redox reactions? Explain with example.
- A student dropped a few pieces of marble in dilute hydrochloric acid contained in a test tube. The involved gas was passed through lime water. What change would be observed in lime water? Write balanced chemical equation for both the changes observed.
- What is meant by photochemical decomposition? Explain with an example.
- Identify the substances oxidised, substances reduced, oxidising agents and the reducing agents in the following reactions
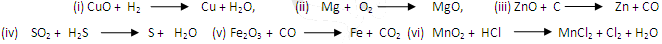
- Write two examples of everyday life, where redox reactions are taking place.
- Food items can be preserved for longer time when kept in refrigerator. What is chemical reason behind this fact?
- Consider the following reaction - NaOH + HCl -------> NaCl + H2O
- What type of reaction is represented by this equation?
- Can this reaction be given any other name also?
- Give reasons for the following -
- Keeping food in air tight containers help in preventing rancidity.
- Moist air and acidic gases are not good for some metals.
- White coloured silver chloride turns grey when kept in sunlight.
- Decomposition reaction called the opposite of combination reaction.
- Can a displacement be a redox reaction?
- Corrosion of aluminium is considered to be advantageous.
- Hydrogen peroxide is kept in coloured bottles.
- Quick lime is used in whitewashing the walls.
- Respiration is considered an exothermic process.
- We cannot stir silver nitrate solution with copper spoon.
- Gold and platinum do not get affected even if there is a presence of moist air and acidic gases.
- What are the two methods which can prevent the rancidity of fatty foods?
- What type of reaction takes place when vegetable matter gets decomposed into compost?
- How will you define rust chemically? Write the steps to prevent rusting.
- Name the agents that can cause corrosion of metals.
- What type of coating is formed on silver articles when they get corroded?
- Write the observations which help us to determine that a chemical reaction has taken place.
- What is a chemical reaction? What is the principle used in balancing the chemical equation?
- What happens during digestion? Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction involved in digestion.
- A lead salt on heating brown fumes. Name the lead compound. What are the brown fumes due to? Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction involved.
- When brown copper powder is heated in a china dish, it becomes black. Name the black coloured compound. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction involved. How can you make it brown again?
- Is corrosion always harmful? Justify your answer with the help of an example.
- What type of salts is formed in precipitation reactions?
  
Submitted By Mr. Sunil D Chauhan
Email Id : [email protected] |
|