![]()
CBSE Guess > Papers > Important Questions > Class XII > 2011 > Economics > Economics By Mr. Pranab Sharma
CBSE CLASS XII
Economics (Revision/Self Assessment test)
Page 2 of 11
- Which of the following is true?
A) II and IIII. A rational choice is always made in the pursuit of social interest.
II. Economics is a social science.
III. Economists try to understand how the economic world works by testing positive statements.
B) Only I
C) Only II
D) Only III
E) I and II- Which of the following is true?
A) Only II. A rational choice is made on the margin.
II. Microeconomics is the study of the national economy while macroeconomics is the study of the global economy.
III. Economists try to understand how the economic world works by testing normative statements.
B) I and III
C) Only II
D) Only III
E) I and II- As technology advances, A) all opportunity costs decrease.
B) the PPF shifts outward.
C) a country moves toward the midpoint along its PPF and can produce more of both goods.
D) all opportunity costs increase.- The PPF shifts inward because unemployment occurs. If a country is operating at a point of production efficiency, A) it enjoys a free lunch when increasing production.
B) it produces on its production possibilities frontier.
C) it must specialize in the production of a good.
D) it operates on its trade line.
E) it cannot be producing at its point of comparative advantage.- Relative to Al, Joe has ________ if Joe can produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than Al. A) a comparative advantage
B) more production efficiency
C) a comparative benefit
D) a marginal benefit
E) a free lunch- Suppose that after specializing according to comparative advantage, a country is trading with another nation that also specializes according to its comparative advantage. Which of the following statements are true for the first country?
A) i only.i. It enjoys gains from trade.
ii. It must have an absolute advantage in the production of the good it produces.
iii. It is producing at a point beyond its PPF.
B) i and ii.
C) i and iii.
D) ii and iii.
E) i, ii, and iii.
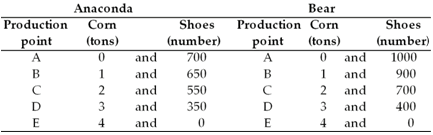
- The table above gives the production possibilities frontier for two countries, Anaconda and Bear. This table shows that A) when Anaconda and Bear specialize and trade, Anaconda should specialize in the production of shoes .
B) when Anaconda and Bear specialize and trade, Anaconda should produce at its production point E.
C) Anaconda has an absolute advantage in the production of corn and shoes.
D) Bear can consume no more than 2 bushels of corn and 700 pairs of shoes.
E) Bear is unable to gain from trade with Anaconda.- The table above gives the production possibilities frontier for two countries, Anaconda and Bear. The table shows that A) Bear achieves production efficiency only at its production point A.
B) Anaconda achieves production efficiency only at its production point A.
C) Anaconda has a comparative advantage in the production of corn.
D) Bear has an absolute advantage in the production of both goods.
E) Both answers A and B are correct.- The table above gives the production possibilities frontier for two countries, Anaconda and Bear. The opportunity cost of moving from production point B to production point C for Anaconda equals ________ and for Bear equals ________. A) 1 ton of corn; 1 ton of corn
B) 650 pairs of shoes; 900 pairs of shoes
C) 550 pairs of shoes; 700 pairs of shoes
D) 100 pairs of shoes; 200 pairs of shoes
E) 50 pairs of shoes; 100 pairs of shoes- The table above gives the production possibilities frontier for two countries, Anaconda and Bear. The opportunity cost of moving from ________ is greater for ________. A) point A to point B; Anaconda
B) point B to point A; Bear
C) point D to point E; Bear
D) point E to point D; Bear
E) any point to any other point; Bear
Submitted By Mr. Pranab Sharma
Email Id : [email protected]