![]()
CBSE Guess > Papers > Important Questions > Class XII > 2012 > Economics > Economics By Mrs. Kritika Bhola
Economics - CBSE CLASS XII
Q.41 If consumers income is 24 & PX= 2 & PY=4. Find out consumer’s equilibrium.
Ans :
Units |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
MUX |
20 |
18 |
16 |
14 |
12 |
10 |
MUY |
24 |
21 |
18 |
15 |
12 |
9 |
Ans : Consumer’s equilibrium is struck when ![]()
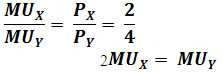
Equilibrium is attained when 2 units of X and 6 units of Y are purchased.
Q. 42 .Discuss the properties of indifference curves.
Ans : 1. Indifference curve always slopes downwards from left to right because when the consumer increases the consumption of one good , he must reduce the consumption of the other good.
2. The IC is strictly convex towards the origin because MRS continuously declines as the consumer moves downward along the IC.
3. Higher IC represents higher utility because of the assumption that preferences are monotonic and more qty. consumed means more utility
Q.43. Distinguish between cardinal and ordinal approach to consumer equilibrium.
Ans :
Cardinal utility |
Ordinal utility |
It is expressed in exact units |
It is expressed in terms of ranking |
Q . 44.Define budget line. State its properties.
Ans :Budget line is the graphical presentation of the whole collection of the combinations of two goods, which costs the consumer exactly his income.
Properties:-
- It is downward sloping straight line because to buy more of one good , the consumer must reduce the purchase of the other good.
- It is a straight line because market rate of exchange between the two goods is constant.
- It is constructed on the basis of consumer’s income and price of both commodities, so change in any one changes the budget line.
Q. 45.
Distinguish between individual demand and market demand..
Ans : Individual demand function shows how demand for a commodity , by an individual consumer in the market, is related to its various determinants
Dx = f ( Px , Pr , Y , T , E )
Where D x : Qty. demanded Px : price of x ; P r: price of related goods; Y : consumer's income; T : Consumer's tastes & preferences; E : consumer's exception
Market demand function shows how market demand for a commodity is related to its various determinants.
Mkt. Dx = f (Px , Pr , Y , T , E , N , Yd )
Where, N: population size ; Yd : distribution of income.
Q .46 .State any 2 factors that affect the demand of a commodity. How do they affect the demand of a commodity?
Ans : 1. Price of commodity: When price of a commodity rises it’s demand decreases and vice-versa.
2. Income of the consumer: The demand for normal goods tend to increase with increase in income and demand for inferior goods tend to decrease with increase in income.
Q . 47 .A and B are substitute goods. Explain the effect of fall in the price of A on demand for commodity B.
Ans:If price of A falls , demand of B will decrease.
Q. 48 . How does the change in income of the household affect the demand for a commodity that it buys?
Ans : The demand for normal commodity will increase and that of inferior will decrease.
Q . 49 .
Distinguish between Substitute goods and complementary goods. Give 2 examples of each.
Ans :
Substitute goods |
Complementary goods |
These are goods which substitute for each other such as tea and coffee, ball-pen and ink-pen |
These are those which complete the demand for each other such as pen and ink, bread and butter |
.Q . 50
Why do household demand more of a commodity at lower price?
Ans :
They are able to purchase more goods from the same income when prices are lower.
Q . 51 .
Distinguish between change in quantity demanded and change in demand. Use diagram
Ans :
Change in qty. demanded refers to increase or decrease in qty. purchased of a commodity in response to decrease or increase in its price , other things remaining constant. There is extension or contraction of demand.
Change in demand of a good is defined as change in demand due to change in the factor other than the price of good. There is backward or forward shift in demand curve.
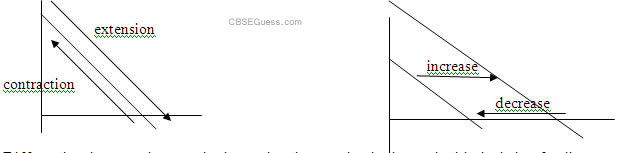
Q. 52 Differentiate between increase in demand and expansion in demand with the help of a diagram
Ans :
Same as above
Q. 53 . Distinguish between decrease in demand and contraction in demand.
Ans : Same as above
Prepared By: Mrs. kritika bhola
[email protected]
