
CBSE Guess > Papers > Question Papers > Class XII > 2006 > Computer Science > Outside Delhi Set - I
Computer science — 2006 (Set I — OutSide Delhi)
Q.1.
- Name the header file to which the following belong: (1)
- pow( )
- random( )
- Illustrate the use of inline function in C++ with the help of an example. (2)
- Rewrite the following program after removing the syntactical error(s), if any. Underline each correction. (2)
#include <iostream.h>
void main( )
{ struct movie
{ char movie_name [20];
char movie type;
int ticket cost = 100;
}MOVIE;
gets(movie_name);
gets(movie_type);
}
- Find the output of the following program: (3)
#include<iostream.h>
#include<string.h>
class student
{ char *name;
int l ;
public:
student( ) {l=0; name=new char I1+1]; }
student (char *s)
{ I =strlen(s); name=new char[I+1];
strcpy (name,s);
}
void display( ) {cout<<name<<endl;}
void manipulate(student & a, student & b)
{ I = a. I + b.I;
delete name;
name=new char[I+1];
strcpy(name, a.name);
strcat(name, b.name);
}
};
void main( )
{ char * temp = “Jack”;
student name1 (temp), name2(” Jill”), name3(”John”),S1,S2;
S1 .manipulate (name1, name2);
S2.manipulate (SI, name3);
S1.display ( );
S2.display ( );
}
- Find the output of the following program:
#include<iostream.h>
void main()
{ long Number = 7583241;
int First=0, Second=0;
do
{ int R=Number%10;
if (R%2==0)
First+=R;
else
Second+=R;
Number /=10;
} while (Number>O);
cout<<First-Second;
}
- What is a default constructor? How does it differ from destructor? (2)
Q. 2.
- What is “this” pointer? Give an example to illustrate the use of it in C++. (2)
- Answer the questions (I) and (ii) after going through the following class:
class Exam
{ int year;
public:
Exam(int y) {year=y;} //Constructor 1
Exam(Exam & t); ///Constructor 2
};
- Create an object, such that it invokes Constructor I. (1)
- Write complete definition for Constructor 2. (1)
- Define a class named HOUSING in C++ with the following descriptions: (4)
Private members
REG_NO integer(Ranges 10 — 1000)
NAME Array of characters(String)
TYPE Character
COST Float
Public Members
- Function Read_Data( ) to read an object of HOUSING type
- Function Display() to display the details of an object
- Function Draw Nos( ) to choose and display the details of 2 houses selected randomly from an array of 10 objects of type HOUSING Use random function to generate the registration nos. to match with REGNO from the array.
- Answer the questions (i) to (iii) based on the following code:
class furniture
{
char Type;
char Model[10];
public:
furniture();
void Read_fur_details( );
void Disp_fur_detailsO;
};
class sofa : public furniture
{
int no_of_seats;
float cost_of_sofa;
public:
void Read_sofa_details( );
void Disp_sofa_details( );
};
class office: private sofa
{
int no_of_pieces;
char delivery_datel10l;
public:
void Read_office_details( );
void Disp_office_details( );
};
void main( )
{ office MyFurniture; }
- Mention the member names which are accessible by MyFurniture declared in main () function. (1)
- What is the size of MyFurniture in bytes? (1)
- Mention the names of functions accessible from the member function Read_office_details () of class office. (2)
Q. 3.
- Write a function in C++ which accepts an integer array and its size as arguments/parameters and assign the elements into a two dimensional array of integers in the following format: (3)
If the array is 1, 2, 3,4,5,6 if the array is 1, 2, 3
The resultant 2 D array is given below The resultant 2 D array is given below
If the array is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
The resultant 2 D array is given below |
If the array is 1, 2, 3
The resultant 2 D array is given below |
1
1
1
1
1
1 |
2
2
2
2
2
2 |
0
0
3
3
3
3 |
0
0
0
4
4
4 |
0
0
0
0
5
5 |
0
0
0
0
0
0 |
1
1
1 |
0
2
2 |
0
0
3 |
- An array MAT [20] [10] is stored in the memory along the row with each element occupying 4 bytes of memory. Find out the base address and the address of element MATE[10][5] if the location of MAT [3][7] is stored at the address 1000. (4)
- Introduction class stack
{ int data [10];
int top;
public:
stack( ) { top=-l }
void push( ); //to push an element into the stack
void pop( ); //to pop an element from the stack
void Delete(int ITEM); //To delete all elements which are equal to ITEM
};
Complete the class with all function definitions. Use another stack to transfer data temporarily. (4)
- Write a function in C++ to perform Insert operation in dynamically allocated Queue containing names of students. (3)
- Write the equivalent infix expression for (2)
10,3, *, 7,1, *, 23, +
Q. 4.
- void main( )
{ char ch=’A’;
fstream fileout(” data.dat”, Ios::app);
fileout<<ch;
int p fileout.tellg( );
cout<<p;
What is the output if the file content before the execution of the program is the string ? “ABC” (Note that” “ are not part of the file) (1)
- Write a function to count the number of blanks present in a text file named “PARA.TXT”. (2)
- Following is the structure of each record in a data file named “PRODUCT.DAT”.
struct PRODUCT
{ char Prodact_Code[10];
char Product_Descriptionil[10];
int Stock;
};
Write a function in C++ to update the file with a new value of Stock. The Stock and the Product Code, whose Stock to be updated, are read during the execution of the program. (3)
Q. 5.
- What are DDL and DML? (2)
- Study the following tables FLIGHTS and FARES and write SQL commands for the questions (i) to (iv) and give outputs for SQL queries (v) to (vi).
TABLE : FLIGHTS
| FL_NO |
STARTING |
ENDING |
NO_FLIGHTS |
NO STOPS |
| IC301 |
MUMBAI |
DELHI |
8 |
0 |
| IC799 |
BANGALORE |
DELHI |
2 |
1 |
| MC101 |
INDORE |
MUMBAI |
3 |
0 |
| IC302 |
DELHI |
MUMBAI |
8 |
0 |
| AM812 |
KANPUR |
BANGALORE |
3 |
1 |
| IC899 |
MUMBAI |
KOCHI |
1 |
4 |
| AM501 |
DELHI |
TRIVANDRUM |
1 |
5 |
| MU499 |
MUMBAI |
MADRAS |
3 |
3 |
| IC701 |
DELHI |
AHMEDABAD |
4 |
0 |
TABLE : FARES
| FL_NO |
AIRLINES |
FARE |
TAX% |
| 1C701 |
Indian Airlines |
6500 |
10 |
| MU499 |
Sahara |
9400 |
5 |
| AM501 |
Jet Airways |
13450 |
8 |
| IC899 |
Indian Airlines |
8300 |
4 |
| 1C302 |
Indian Airlines |
4300 |
10< |
| 1C799 |
Indian Airlines |
10500 |
10 |
| MC101 |
Deccan Airlines |
3500 |
4 |
- Display FL_NO and NO_FLIGHTS from “KANPUR” to “BANGALORE” from the table FLIGHTS.
- Arrange the contents of the table FLIGHTS in the ascending order of FL_NO.
- Display the FLNO and fare to be paid for the flights from DELHI to MUMBAI using the tables FLIGHTS and FARES, where the fare to be paid = FARE +FARE*TAX%/100.
- Display the minimum fare “Indian Airlines” is offering from the table FARES.
- SELECT FL_NO, NO_FLIGHTS, AIRLINES from FLIGHTS, FARES where STARTING=”DELHI” and FLIGHTS.FL_NO=FARES.FL_NO.
- SELECT count (distinct ENDING) from FLIGHTS. (6)
Q. 6.
- State and verify Associative Law. (2)
- Write the equivalent expression for the following logical circuit: (2)
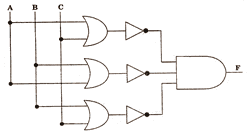
- Express P+Q ’R in POS form. (1)
- Reduce the following Boolean expression using K-Map: (3)
F(P, Q, R, S) = π (0,3,5,6,7, 11, 12, 15)
Q. 7.
- Name two transmission media for networking. (1)
- Expand the following terms: (2)
- XML
- GSM
- SMS
- MAN
- Differentiate between Hackers and Crackers. (1)
- INDIAN PUBLIC SCHOOL in Darjeeling is setting up the network between its different wings. There are 4 wings named as SENIOR(S), JUNIOR(J), ADMIN(A) and HOSTEL(H).
Distance between various wings are given below:
| Wing A to Wing S |
100m |
| Wing A to Wing J |
200m |
| Wing A to Wing H |
400m |
| Wing S to Wing J |
300m |
| Wing S to Wing H |
100m |
| Wing J to Wing H |
450m |
Number of Computers
| Wing A |
10 |
| Wing S |
200 |
| Wing J |
100 |
| Wing H |
50 |
- Suggest a suitable Topology for networking the computer of all wings. (1)
- Name the wing where the Server is to be installed. Justify your answer. (1)
- Suggest the placement of Hub/Switch in the network. (1)
- Mention an economic technology to provide internet accessibility to all wings. (1)
| Computer Science 2006 Question Papers Class XII |
| Delhi |
Outside Delhi |
Compartment Delhi |
 |
Set I |
 |
Set I |
 |
Set I |
|
|